How to Conduct a Risk Assessment

Assessing risk is important to protect individuals, assets, the environment, etc. Risk assessment is a key element of broader risk management strategies and is used across multiple sectors. If you want to learn about how to conduct a risk assessment, we have a few basic guidelines to help you get started.
What is Risk Assessment?
Risk assessment includes analyzing and identifying events that can possibly lead to a mishap or a negative impact for assets, individuals, and the environment and involves performing a risk analysis to help evaluate and mitigate risks.
Risk assessment can be viewed across various sectors, within an organization, and even at the household level. Hence, risk assessment is a systematic process for the evaluation of future events that can lead to potential hazards. Be it risks to a business, its employees, the environment, human settlements, during an emergency response or risks related to a project, to information security, commercial outdoor activities, etc.
The video below provides an example of risk assessment for the health and safety of employees at the workplace.
5 Step Risk Management Process Identify Hazards
Risk management can be performed for mitigating risks. The 5-step risk management process for identifying hazards is used by organizations for identifying hazards, assessing risks, controlling risks, recording findings, and reviewing controls.
1. Identifying Risks
The first step that an organization needs to take to manage risks is to identify hazards. This involves understanding the type of risk that might need mitigation. Risks can involve health and safety risks to employees, market risks, regulatory risks, compliance risks, etc.
2. Analyzing Risks
Once risks have been identified, they need to be analyzed for their potential severity and likelihood. Does a risk have the potential to pose a significant financial loss, impact the business legally, lead to loss of time or resources? High risks with a likelihood of occurring are to be prioritized for mitigation.
3. Evaluating Risks
As organizations have limited resources, it might not be possible to try to prevent every risk. For example, if your organization assesses a small chance of a flood leading to damage to your factory, where relocation is extremely costly and floods in the area have not occurred in three decades, would you try to mitigate such a risk? Risks that seem unlikely or have a chance of not posing serious loss are less likely to gain attention as compared to serious risks that are likely to occur and might lead to an imminent hazard. For this purpose, a Risk Benefit Analysis template can be used to present the conclusions of a risk evaluation process.
4. Controlling Risks
Once high-priority risks have been singled out, steps can be taken to control them. This would involve implementing risk evaluation decisions to control the risks that seem likely to lead to a hazard. For example, if a risk of injury to employees is identified due to a production process, steps can be taken by employing safety equipment, training employees to prevent the potential hazard, or even finding alternative ways for performing the task safely.
5. Reviewing the Risk
Organizations can continue to evaluate the risks by analyzing available data. Some risks cannot be completely eliminated, such as market risks, a risk of a competitor taking away more of your market share, or an economic meltdown leading to heavy losses. Businesses can continue to prioritize risk reduction measures based on these evaluations.
Risk Assessment Techniques
Organizations use different risk assessment techniques, criteria, and tools. Some examples of risk assessment techniques are mentioned below.
You can also present any of the below-mentioned analysis by using a risk-themed PowerPoint template with readymade layouts to design and present a risk assessment matrix or download this risk assessment matrix slide. Different third-party PowerPoint template providers like SlideModel and FPPT also provide suitable templates tailored for the following and other risk assessment techniques.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT Analysis analyzes the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for an organization. The analysis is a good way to determine not only potential risks but also opportunities, strengths, and weaknesses that might weigh down an organization.
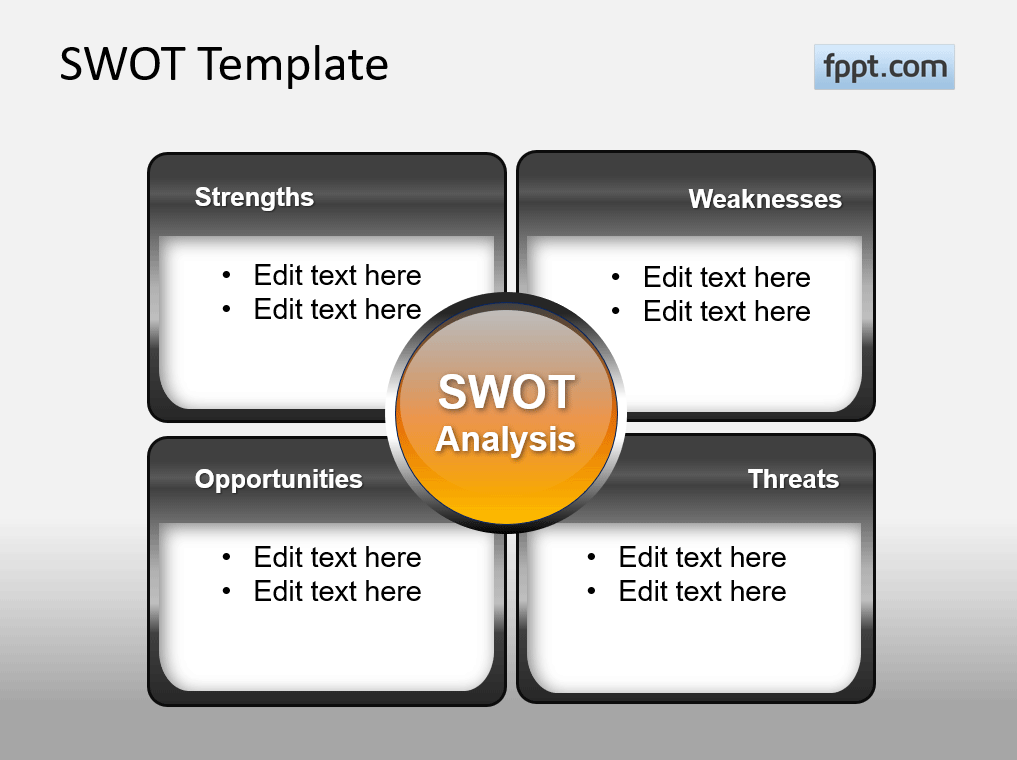
Source: Free SWOT PowerPoint template by FPPT
PESTEL Analysis
A PESTEL analysis looks at political, economic, sociological, technological, legal, and environmental factors that might influence an organization. It is a framework used in strategic management to assess external factors and their effects.
Individuals can use PESTEL PowerPoint templates to present the results of a PESTEL analysis to an audience.
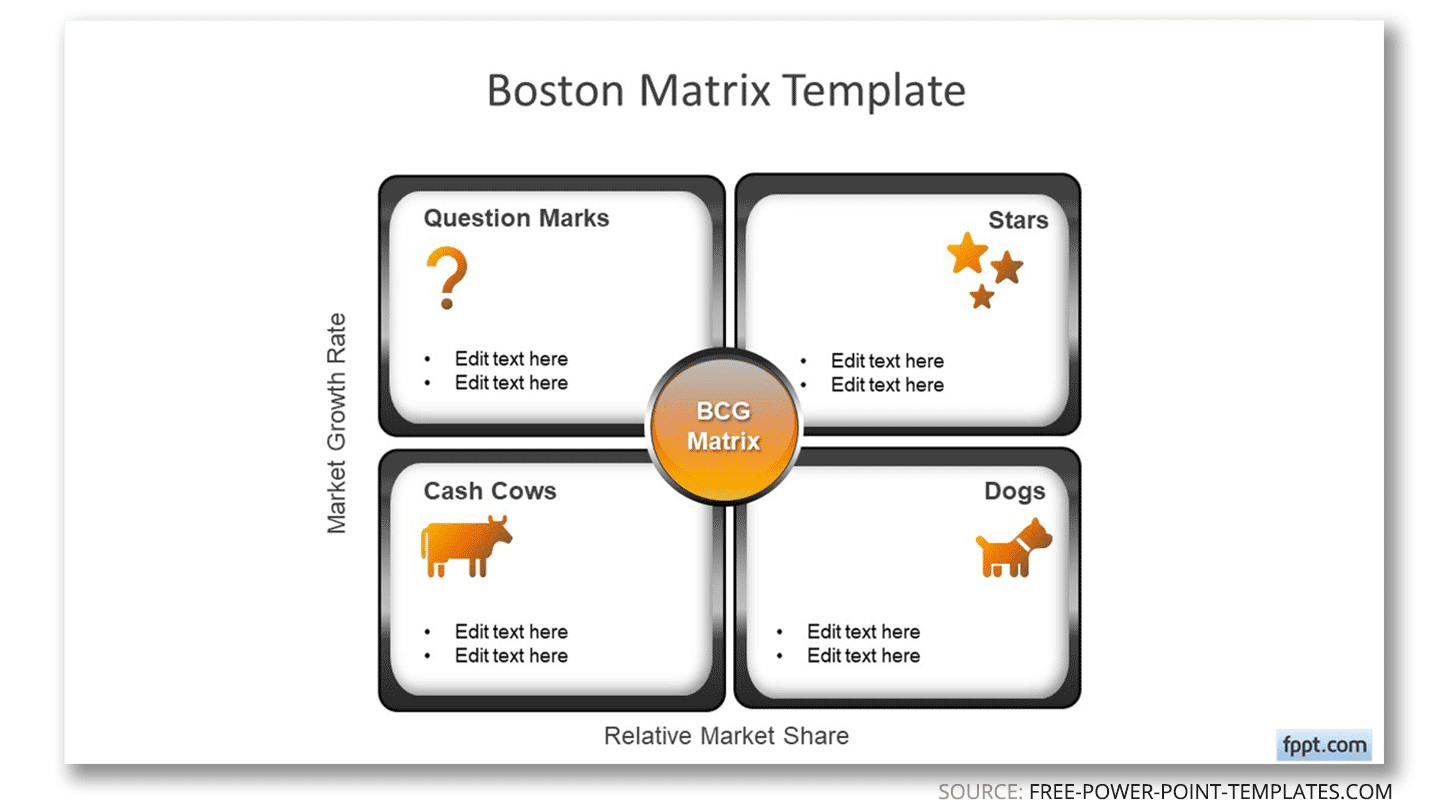
Boston Matrix
A Boston Matrix is used for assessing the portfolio of a business. The matrix consists of stars which are the top-performing products, cash cows that have the potential to be milked to fund other ventures because of their longevity, question marks that are problematic products that need to be analyzed for further action, and dogs that are products that haven’t performed according to expectations.
The following free BCG Matrix template for PowerPoint can help you to make this analysis very easy.
RAIDAR Model
The RAIDAR Model is a risk assessment identification and ranking model. RAIDAR stands for risks, assumptions, issues, dependencies, action, and repairs.
Final Words
Risk assessment is key for businesses looking to identify and mitigate risks. It can also be performed in various other sectors such as when deploying software, during emergency response measures, disaster risk reduction, and even informally at the household level by an individual. Keeping the five basic elements of risk management in view, you can identify risks, analyze their potential and likelihood, evaluate, control and continue to review them.
