How to Delight Your Customers using the Kano Model

Developing a product that fulfills customer needs and delights them requires carefully analyzing various customer needs and market demand for features that might give your product an edge. The Kano model presents a framework for analyzing and catering to customer demands by analyzing different essential aspects of a product.
What is Kano Model?
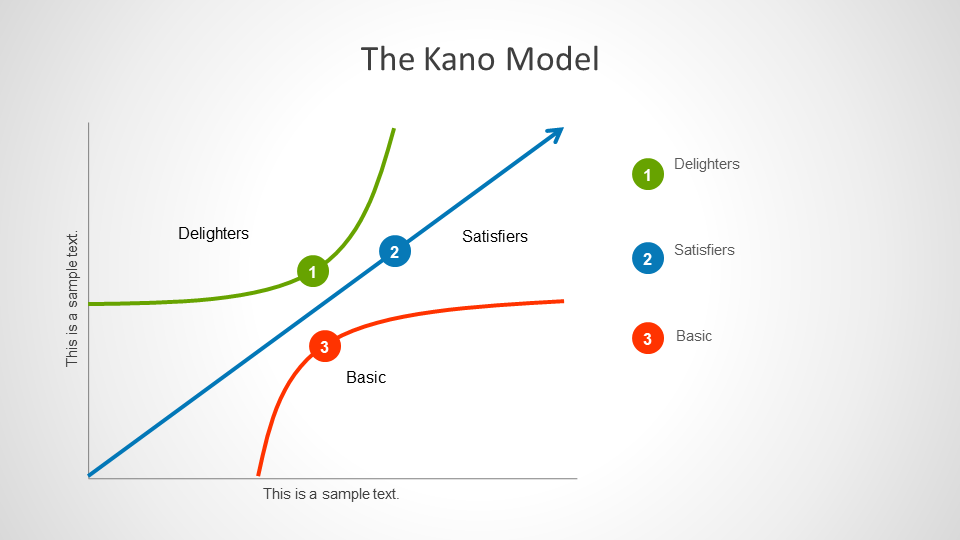
The Kano model is named after Noriaki Kano, who developed the model which is used for classifying customer preferences based on five categories. The Kano model is a product development and customer satisfaction theory which categorizes products with expected quality (Must-be Quality), basic features which if not provided lead to dissatisfaction (One-dimensional Quality), attractive features (Attractive Quality), features that customers are indifferent to (Indifferent Quality) and features which might lead to customer dissatisfaction (Reverse Quality). These categories are also attributed to different names such as delighters, satisfiers and dissatisfiers.
Source: Kano Model PowerPoint template by SlideModel
Applications of Kano Model and Kano Analysis
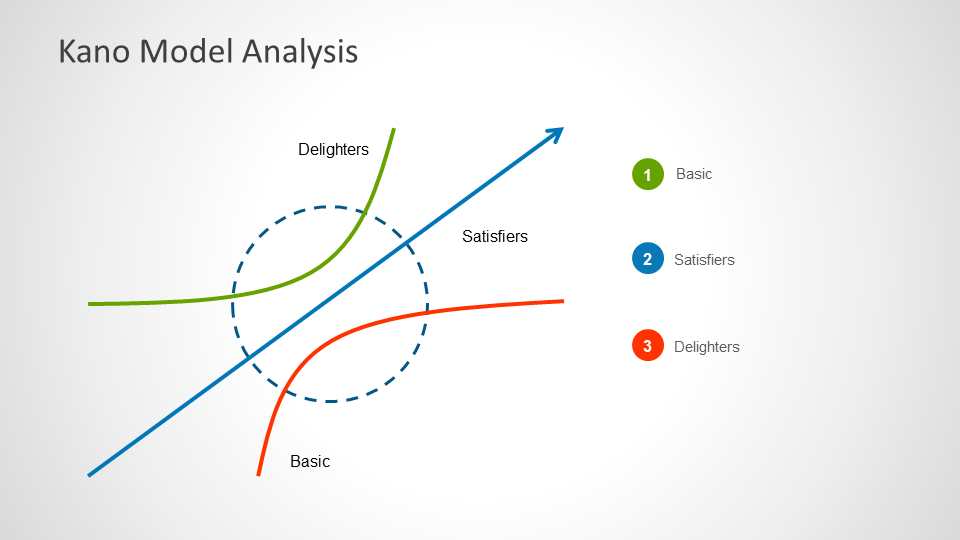
The Kano model can be used for understanding customer needs and to better position your product based on its features which might delight customers. When using the Kano model, you will need to draft the list of customer requirements, use questionnaires for gathering feedback, evaluate customer feedback and create a diagram to show your analysis. However, in order to do all that you need to first understand the five categories of the Kano model. You can perform a Kano analysis by plotting basic features, satisfiers and dissatisfiers as a diagram, based on customer preferences and your market analysis. You can also create an evaluation table with features that the customers might like, dislike, expect or don’t care about.
Source: Kano Model PowerPoint template by SlideModel
Below is an explanation of how the Kano model can be implemented using the five categories of the model. Based on these you can perform your Kano analysis to understand what basic features might be expected by your customers, as well as the delighters, expected features, as well as the features which might lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Related: How to Create a Kano Model Diagram in PowerPoint
1. Does Your Product Fulfill the Must-be Quality Requirements?
In the Kano model, Must-be Quality refers to the features that are expected from a product. These are the basic product requirements, which if not included can have a devastating impact and lead to the failure of the product. For example, when you buy a smartphone you expect to be able to make calls, use the Internet, take pictures and install apps from an app store. Imagine a modern smartphone without any of these features. Would such a smartphone be successful? Must-be Quality is therefore the basic requirements that are expected of a product by a customer. You must carefully analyze these requirements when designing a product or before starting a service.
2. Your Product Must Account for One-dimensional Quality
One-dimensional quality are the features that can lead to customer satisfaction if fulfilled and dissatisfaction if not fulfilled. A customer might check into a hotel and order lunch, if the food takes longer than expected to arrive or if the customer has to call multiple times to ask for it, this will lead to customer dissatisfaction. However, the timely arrival of the food will be considered as normal by the customer and will not win the hotel any extra points. Similarly, clean towels and a tidy room are expected features for a customer checking into a hotel. Not having these will lead to customer dissatisfaction.
3. Does Your Product Have Attractive Qualities?
Attractive qualities are the factors that give your product an edge. These are the attributes that delight your customers and win you extra points for your product. A food delivery service which provides a discount every time a customer order is incorrectly delivered is not a feature expected from such a service, however provision of such a discount will delight customers.
4. Customers Might be Indifferent to Some Features (Indifferent Quality)
There are certain features of a product or service which customers are often indifferent to. A product might come with boxes and wrappers made of high-quality material, but customers might be simply indifferent to it. Factors like these which have no impact on the customer should be eliminated or reduced to save costs. Especially, if they are unlikely to affect the quality of the product. In the case of the aforementioned, if a less costly wrapping material can retain the same product quality, then using more expensive material will be a waste of resources.
5. Reverse Quality Might Lead to Customer Dissatisfaction
You might have come across customer support that is too pleasant, even when nothing gets actually done. These are the kind of attributes that can lead to customer dissatisfaction. Unnecessary pleasantries, elaborate service rituals and extra product features that have no real value can in fact lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Alternatives to Kano Model
There are a number of Kano model alternatives that you can use for prioritizing product features and understanding what might click with your customers. We have compiled a list of a few suggested Kano model alternatives below.
RICE Scoring Model
The RICE scoring model is used as a framework for prioritizing the products, initiatives or features that product managers prioritize based on the acronym RICE, i.e. reach, impact confidence and effort. The model can be great for prioritizing project ideas in order to eliminate personal bias and give priority to the most promising products, features and initiatives.
Value vs. Complexity Matrix
This is another prioritization model that looks at what to prioritize on a product roadmap. Using this technique, a product team builds a graph that shows a prioritization matrix with complexity/effort and business value. The graph shows the anticipated value of each initiative relevant to the effort required.
MoSCoW Prioritization
MoSCoW prioritization or MoSCoW analysis is a prioritization model that accounts for the must-haves, should-haves, could-haves, and wish or will not have at this time. The model requires key stakeholders and the product team to align objectives and factors for prioritization before the MoSCoW analysis starts. This is followed by the prioritization of initiatives.
Kano Model PowerPoint Template
If you want to create a comprehensive Kano model presentation, you can use this Kano Model PowerPoint Template. With four Kano diagram slides, the template gives you the option to plot your Kano model using basic, satisfiers and dissatisfiers. You can also use drag and drop to adjust these factors to customize your Kano model diagram.
Go to Download Kano Model PowerPoint Template
Final Words
Based on the five categories of the Kano model, a product can be assessed based on the basic features, delighters, satisfiers and dissatisfiers to help determine what might be the best mix of features to attract customers. While the model itself is straightforward, it requires careful consideration for customer needs and wants. In order to be effective and accurate in performing a Kano analysis that truly reflects aspirations of customers and the unique selling point that can help make a product stand out.